Science Based Health Benefits of Collagen
Collagen supplements seem to be everywhere – you’ll find them in skin creams, body lotions, powders, capsules and even snack bars. But do collagen supplements actually help? Here’s the lowdown supported by evidence based research.
What is Collagen?
Collagen is the most abundant protein in our bodies. It is one of the major building blocks of bones, muscles, joints and tendons providing strength and structure. It also provides support to our skin, hair and organs.
The word “collagen” comes from the Greek word for glue: collagen is a structural protein that binds cells and tissues together while helping them maintain shape and integrity.
Collagen proteins are produced by animal connective tissue cells called fibroblasts. For a protein to be classified as a collagen, it must form the collagen-like triple helix and provide structural support in the extra cellular matrix. This is a diverse mesh of proteins and sugars produced by certain cells, which acts as the mortar binding our cells together.
Collagen is made up of many amino acids, primarily glycine, proline, alanine, hydroxyproline, and glutamic acid. Foods containing lots of collagen also contain high glycine levels. Glycine helps to protect the vascular system, as it is able to decrease inflammation. It can also be beneficial for sleep.
There are different types of collagen; some are derived from animal bones or skin, and others from animal cartilage. Most of the studies are based on Bovine Collagen.
Humans have 28 different types of collagen proteins. Over 80% of collagen is type I, II, or III, which are found mainly in the skin, bones, tendons, cartilage, lungs, intestines, and vascular system. Type IV is also common and particularly important for skin health.
- Type I collagen accounts for 90% of the body’s collagen. This is particularly important for support healthy skin, bones, tendons, fibrous cartilage, connective tissue.
- Type II collagen is found in elastic cartilage, which cushions joints.
- Type III collagen provides support for arteries, organs and muscle.
- Type IV collagen is more associated with skin health.
Our bodies are able to make collagen using amino acids (glycine and proline) in combination with vitamin C and copper. As you age, your body produces less and lower-quality collagen which can in turn contribute to some of the noticeable signs of ageing such as wrinkles. Cartilage also weakens with age which can make us more vulnerable to injury, stiffness and pain.
There are certain dietary patterns that can interfere with the production of collagen. Excess sugar and carbohydrates in the diet, uv sun damage, smoking and certain health conditions such as lupus.
You can increase your intake of collagen with certain foods too. Of particular note is bone broth which is rich in gelatine.
Hydrolysed collagen is a popular supplement. Hydrolysed means that the amino acids in collagen have been broken down so that they’re more easily digested and absorbed.
Research has demonstrated many benefits from taking collagen supplements.

Muscle Mass
As collagen is a major component of muscle tissue, collagen supplementation can improve muscle mass, strength and body composition. Collagen comprises a number of amino acids including glycine which is important for the production of creatine in the body. This can provide fuel to the muscles during a workout making it ideal pre and post workout.
Studies have shown collagen supplementation can improve muscle strength and body composition after training.
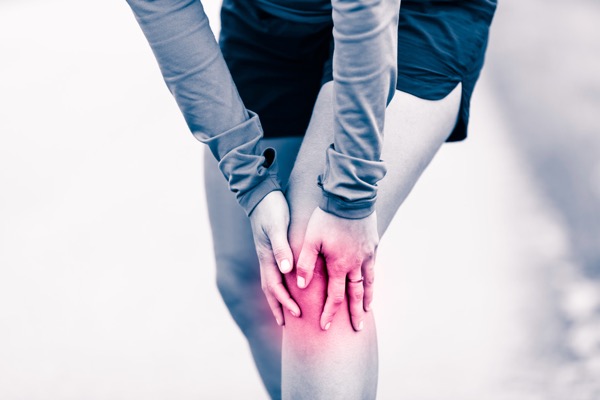
Joint Health / Recovery
As we age our cartilage weakens and gradually deteriorates. This can lead to stiffness, muscle soreness and joint pain. Studies have shown collagen supplements can help aid recovery and help relieve joint and knee pain especially post exercise.
One study for example demonstrated supplementation with type II collagen improved recovery in athletes with ankle problems and reduced sprains and other injuries.
Research has demonstrated the use of collagen supplements for reducing stiffness associated with osteoarthritis and lowering inflammation associated with rheumatoid arthritis.
Being an essential protein in the bone, collagen is also essential for maintaining optimal bone health particularly as you age.

Skin Health & Cellulite
Since collagen is an essential protein providing elasticity to the skin many people take collagen to maintain a healthy more youthful skin. The glycine and hydroxyproline peptides appear to be important for skin health by inhibiting collagen breakdown.
Studies have shown supplementation can improve skin elasticity and reduce wrinkles. As well as keeping your skin youthful collagen may also help improve the appearance of stubborn cellulite. One study demonstrated collagen peptide supplementation showed significant improvement in skin texture.
Gut Health
One of the less researched areas is the use of collagen for gut health. Collagen may be helpful to support the gut’s connective tissue providing support to the lining of your digestive tract. Supplementation may also have potential to lower inflammation and improve overall digestive health.

Sleep
Collagen is naturally rich in glycine and some studies have demonstrated improvements in sleep with glycine supplementation so for some people it may be useful to take a scoop of collagen prior to bedtime.

What Nutrients Can Help with Collagen Production?
Several nutrients are important for the production of collagen. These include vitamin C, Lysine and Proline, Niacin (B3) and vitamin A.
Silicon is a trace nutrient that is also involved in collagen production. Silicon increases collagen production and the amount of an enzyme needed to make collagen in cartilage and bone cells.
How much collagen is beneficial?
The research studies have used varying amounts of collagen and the range needed will depend on your goals. Looking at some of the studies on joint health studies have used anything from 40mg daily of collagen peptides to 10g daily while for body composition and muscle strength more has been shown to be beneficial (15g daily) For skin health studies have used around 2.5-5g daily.
Choose hydrolysed collagen as this is more easily digested and absorbed into the body.

